
What Is MDF? | Properties, Material, Construction & Strength
Posted by Lee Watkinson on 9th May 2025
Medium-Density Fibreboard (MDF) is an engineered wood product that shapes more of our interior world than you know. From skirting boards to furniture, MDF provides a stable, uniform alternative to natural timber, though with distinct properties worth understanding before your next project.
Note: This guide aims to provide objective information about MDF, its properties, and applications. We'll examine both advantages and limitations to help you make informed decisions for your interior projects.

What exactly is MDF?
Medium-Density Fibreboard (MDF) is an engineered wood panel product manufactured from wood fibres mixed with a synthetic resin binder and pressed under heat and pressure into flat sheets. Unlike natural wood, MDF is entirely homogenous, it has no grain, knots, or natural defects.
The average composition of standard MDF comprises approximately 80% wood fibres by mass, 9-10% resin binder (usually urea-formaldehyde), with the remainder being water (8-9%) and small amounts of paraffin wax (≤2%) for improved moisture resistance.
The density of MDF typically ranges between 600-800 kg/m³, placing it between particleboard (less dense) and High-Density Fibreboard (more dense). This property significantly influences its strength, weight, and performance characteristics.
MDF first entered commercial production in the 1960s, with the first dedicated factory established in New York in 1965. Europe's first MDF was produced in 1973, with large-scale capacity expanding from the late '70s. Initially marketed for the furniture industry, it gained traction in joinery and architectural applications with the introduction of moisture-resistant variants in the late 1980s.
How MDF is manufactured
The journey from tree to the smooth MDF sheet involves a sophisticated engineering process. Understanding this helps explain MDF's unique properties and consistent performance.
Wood preparation
The process begins with raw wood material, typically residuals from other wood processing industries like sawmilling (chips, sawdust, shavings) or from sustainable forestry sources. Logs are debarked, then fed into chippers to create uniform wood chips.
Fibre production
Wood chips are washed, then softened with steam before being mechanically broken down into individual fibres in a defibrator. This 'defibration' process distinguishes MDF as a 'dry process' fibreboard, breaking wood into its constituent fibres while keeping them largely intact.
Fibre treatment
The separated fibres enter a 'blowline' where additives are introduced, typically paraffin wax first for moisture resistance, followed by the resin binder (e.g., urea-formaldehyde). The mixture is dried in a heated chamber, resulting in a fluffy, lightweight fibre ready for forming.
Mat forming
The resinated fibres are evenly distributed onto a moving belt to form a continuous mat. This random distribution of fibres contributes to MDF's homogeneous structure and uniform properties in all directions, unlike natural wood's directional properties.
Hot pressing
The fibre mat undergoes pre-compression before entering a hot press. Under intense heat and pressure, the resin cures, bonding the fibres together into a rigid panel. Modern facilities often use a continuous press process, creating a slight density profile, higher density near the surfaces for better mechanical properties.
Finishing
After pressing, the hot panels are cooled, then sanded to achieve the characteristically smooth, flat surface that makes MDF ideal for finishing. Finally, the large master panels are cut to standard industry dimensions (e.g., 2440 x 1220 mm in the UK/EU market).
This controlled manufacturing sequence is directly responsible for MDF's defining attributes. The defibration and random mat forming create homogeneity, eliminating natural wood defects. Hot pressing ensures density and stability, while sanding provides the smooth surface perfect for painting or veneering.
The process yields panels in various thicknesses, typically from around 3mm up to 40mm or more, catering to diverse applications from thin decorative panels to substantial structural elements.
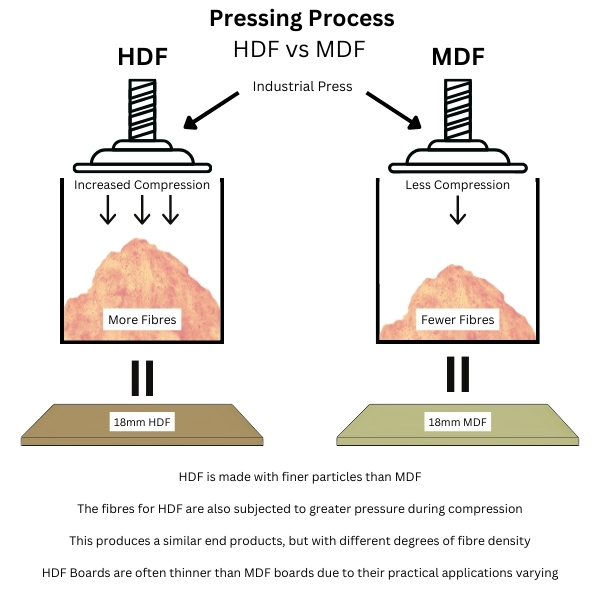
Types and grades of MDF
MDF comes in various specialised types, each engineered with specific properties to suit different applications and environments. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the appropriate material for your project.
Other specialised MDF variants
- High-Density Fibreboard (HDF): Density exceeding 800 kg/m³, offering greater strength, hardness, rigidity, and improved screw holding capacity. Excellent for demanding applications like laminate flooring substrates.
- Ultra-Light MDF: Lower density (below 600 kg/m³) for easier handling and installation. Suitable for non-structural decorative elements where weight is a concern.
- Exterior MDF: Formulated with highly durable water-resistant resins for external applications. Requires proper coating and maintenance. Medite Exterior is a well-known example.
- Zero Added Formaldehyde (NAF/NAUF): Manufactured using alternative binding systems that contain no added formaldehyde, such as pMDI. Used where low emissions are critical, like schools and hospitals.
- Pre-finished MDF: Panels supplied with factory-applied primer, decorative paper, or melamine facing for time savings and enhanced performance.
Industry standards and certifications
MDF products sold in the UK must comply with specific standards ensuring quality, safety, and performance:
- BS EN 13986: The key European standard governing wood-based panels for construction. Compliance is a legal requirement for market access.
- BS EN 622-5: Specific requirements for dry process boards (MDF), defining technical classes based on intended use and properties.
- UKCA Marking: Required conformity marking for products placed on the Great Britain market, indicating compliance with applicable regulations.
- Formaldehyde Emission Classes: E1 is the mandatory minimum standard in UK/EU (≤0.1 ppm). Lower emission options include E0, CARB Phase 2, and NAF (No Added Formaldehyde).
- FSC/PEFC Certification: Verifies that wood fibres come from responsibly managed forests through independent, third-party certification.
Note: When selecting MDF, always check the manufacturer's technical datasheet for specific performance characteristics and certifications relevant to your application.
MDF vs. alternatives
Understanding how MDF compares to other common wood materials helps in making informed decisions for specific applications. Each material provides a distinct balance of properties, cost, and suitability.
MDF advantages over solid wood:
- More dimensionally stable with less warping or twisting
- No knots, splits, or grain inconsistencies
- Smoother surface ideal for painting
- Consistent properties in all directions
- Significantly more affordable than hardwoods
- Available in wider panels and longer lengths
- Efficiently utilises wood resources
Solid wood advantages over MDF:
- Superior strength and impact resistance
- Better screw holding capacity, especially on edges
- Natural beauty of grain for staining/clear finishes
- Better moisture recovery (can dry out without losing integrity)
- More readily repaired, refinished, and recycled
- Lighter weight for some species
- Certain species suitable for exterior use
| Feature | MDF | Particleboard/Chipboard | Plywood |
|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fine wood fibres, resin binder | Larger wood chips/particles, resin binder | Cross-laminated wood veneers |
| Strength | Moderate | Low (prone to sagging) | High (especially in bending) |
| Surface | Very smooth, uniform | Coarse, porous | Varies by grade (visible grain/layers) |
| Edge quality | Smooth but porous (needs sealing) | Poor (crumbly, requires banding) | Shows layers, can splinter |
| Machinability | Excellent (smooth cuts, fine details) | Fair (prone to chipping) | Good (can splinter at edges) |
| Weight | Heavy | Medium | Medium-Light |
| Moisture resistance | Poor (Standard), Better (MR grade) | Very poor | Fair to excellent (depends on grade) |
| Cost (relative) | Medium | Low | Medium-High |
Best applications by material:
- MDF: Painted furniture, cabinet doors, architectural mouldings, decorative panels, interior trim
- Particleboard: Budget furniture carcasses, substrate under laminates, shelving in utility spaces, underlayment
- Plywood: Structural applications, furniture carcasses, flooring substrate, boats, high moisture areas, visible wood grain applications
- Solid Wood: Fine furniture, exposed structural elements, high wear surfaces, outdoor applications, stained or clear-finished items
Properties and performance
Understanding MDF's specific physical and mechanical properties helps predict its performance and suitability for various applications.
Mechanical properties
Screw holding capacity is another critical property. MDF holds screws well on its face (1000-1200 N), but less effectively on edges. Pre-drilling and using the correct screw types are essential for optimal performance.
Physical characteristics
Dimensional stability
MDF expands and contracts with humidity changes, but uniformly in all directions (unlike solid wood's anisotropic movement). Typical linear expansion is around 0.3%-0.4% for significant humidity shifts. Good stability for interior applications with normal humidity variations.
Moisture resistance
Standard MDF is susceptible to moisture damage. Thickness swelling after 24-hour water immersion typically 10-15% (EN 317 test). MR grades show significantly better performance (7-12% swelling). Neither is waterproof, all MDF requires proper sealing for maximum moisture protection.
Environmental performance
Common applications
MDF's unique combination of properties makes it the material of choice for numerous applications, particularly where a smooth, uniform finish is desired.
Other common uses
- Commercial Displays: Shopfitting elements, retail displays, exhibition stands, and point-of-sale units
- Doors: Interior door cores, often with a veneer or laminate facing
- Substrate: Base layer for veneering, laminating, or other decorative finishes
- Speaker Enclosures: The dense, uniform structure provides excellent acoustic properties for audio equipment
- Crafting & Models: Templates, jigs, architectural models, and other precision applications
Working with MDF
MDF's performance during machining, finishing, and installation significantly affects the quality of the end result. Proper techniques and precautions are essential for successful outcomes.
Machining MDF
MDF is renowned for its excellent machinability, stemming from its homogeneous composition. Unlike natural wood, it has no grain direction to contend with, no knots to interrupt cuts, and it does not splinter easily. This allows for clean, sharp edges and intricate profiles.
However, MDF is significantly more abrasive than most natural woods due to its high density and resin content. This leads to faster tool wear, making the use of carbide-tipped tools essential for good results and reasonable tool life.

Key machining recommendations:
- Cutting: Use carbide-tipped blades with a high tooth count. Support the sheet fully to prevent vibration and binding. For straight cuts, consider using a guide rail or fence.
- Routing: MDF excels when routed, allowing for crisp details and complex profiles. Again, carbide router bits are necessary. For deep profiles, make multiple shallow passes rather than a single deep cut.
- Drilling: Pre-drilling pilot holes is generally recommended before inserting screws, particularly near edges, to ensure the best hold and prevent any bulging.
- Dust extraction: MDF produces copious amounts of very fine dust during machining, posing both a workshop cleanliness issue and a health hazard. Effective dust extraction at the source is mandatory.
Finishing MDF
MDF's finishing characteristics are a key reason for its popularity, particularly its suitability for painted finishes.
Despite its smooth appearance, MDF is porous and will absorb paint unevenly if not properly primed. Edges are particularly absorbent, requiring special attention. Proper preparation is essential for a professional finish.
Surface preparation
Sand all surfaces with 180-220 grit sandpaper. Pay particular attention to edges, which should be sanded with 240 grit or finer for maximum smoothness. Remove all dust thoroughly with a vacuum and tack cloth.
Edge treatment
Edges require special attention as they're far more absorbent than faces. Options include: applying a thin skim coat of wood filler, using diluted PVA glue (50:50 with water), applying multiple primer coats specifically to edges, or using edge banding for a more durable finish.
Priming
Apply a suitable primer designed for MDF. Options include water-based acrylic primers (quick-drying, low odour), solvent-based primers (excellent sealing properties), or shellac-based primers (very fast drying, excellent sealing). Apply 1-2 coats, sanding lightly between coats with 220-320 grit.
Painting
Apply your chosen paint using high-quality synthetic brushes, foam rollers, or spray equipment for the smoothest finish. Apply in thin, even coats, allowing adequate drying time between coats. Light sanding between topcoats can further enhance smoothness. Water-based acrylic paints work well, with satin or semi-gloss finishes being popular choices.
Health and safety considerations
Working with MDF requires specific health and safety precautions, particularly regarding dust management. The Health and Safety Executive (HSE) in the UK provides clear guidance under the Control of Substances Hazardous to Health (COSHH) regulations.
Key health and safety measures:
- Dust extraction: Use local exhaust ventilation (LEV) connected to an M-Class (or higher) rated extraction system to capture dust at the source.
- Respiratory protection: When dust cannot be completely controlled, wear appropriate respiratory protective equipment (RPE). The minimum recommended level is FFP3 for disposable masks or P3 filters for reusable masks.
- Other PPE: Safety glasses protect eyes from dust and debris. Gloves can prevent skin irritation.
- Work practices: Avoid brushing or using compressed air to clean up dust. Instead, use vacuum extraction with an appropriate filter.
- Ventilation: Ensure good general ventilation in the workspace in addition to local extraction.
According to the HSE:
"Wood dust can cause serious health problems. It can cause asthma, which carpenters and joiners are four times more likely to get compared with other UK workers. Wood dust can also cause other lung diseases, and nose cancer." HSE Woodworking Guidance
Environmental considerations
The environmental aspects of MDF encompass its raw material sourcing, manufacturing impacts, potential health concerns, and end-of-life management.
Sustainability and carbon footprint
Resource efficiency
A significant environmental advantage of MDF is its efficient utilisation of wood resources. It's often manufactured using sawmill co-products (chips, sawdust, shavings) and forestry thinnings that might otherwise be wasted. It can also incorporate recycled wood content and utilise wood from fast-growing plantation species.
Carbon storage
Wood products play a role in climate change mitigation by storing carbon dioxide absorbed during tree growth. This carbon remains sequestered within the MDF panel throughout its service life. Approximately half the mass of dry wood is carbon, making MDF a significant carbon store.
Environmental impact
Manufacturing MDF is energy-intensive and uses synthetic resins. Life cycle assessments show that raw material extraction (especially resin production) and the manufacturing process are the primary contributors to environmental impacts. Using renewable energy in production significantly improves the overall environmental footprint.
Formaldehyde emissions
Formaldehyde emissions from MDF have historically been a key environmental and health concern, primarily due to the traditional use of urea-formaldehyde (UF) resins as the binder.
All MDF legally sold for interior use in the UK must meet the E1 emission standard (≤0.1 ppm). However, voluntary lower emission options are increasingly available, including E0, CARB Phase 2, and NAF (No Added Formaldehyde) products.
| Standard | Emission Limit | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| E1 | ≤0.1 ppm (0.124 mg/m³) | Mandatory minimum for UK/EU interior use |
| E0 | ≤0.07 ppm | Voluntary lower emission classification |
| CARB Phase 2 | ≤0.11 ppm | US standard, similar to E1, widely adopted globally |
| NAF/NAUF | ~0.04 ppm | No Added Formaldehyde, uses alternative resins |
Beyond selecting lower-emission boards, practical measures to manage formaldehyde exposure include good ventilation during and after installation, and sealing surfaces and edges with primers, paints, laminates, or veneers.
From the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC):
"Formaldehyde is classified as a Group 1 carcinogen, which means that there is sufficient evidence that it can cause cancer in humans." IARC Classification
Recycling and end-of-life
The disposal and potential recycling of MDF waste is an area of increasing focus. Traditionally, options have been limited to landfill or incineration, neither ideal from an environmental perspective.
Recent advances:
UK-based company MDF Recovery Ltd has developed technology to recycle waste MDF by breaking down the resin binder without damaging the wood fibres. The recovered fibres can be reused in new MDF production (tested at up to 20% replacement) or for other applications like thermal insulation.
This technology represents a significant step towards a circular economy for MDF, potentially transforming it from a largely single-use material to one with a closed-loop lifecycle. As these recycling facilities become more widespread, the environmental profile of MDF will continue to improve.
According to a study in the journal Fibres:
"Developments in MDF recycling technology are pivotal for the circular economy and environmental sustainability of the wood panel industry. They transform what was previously considered a waste stream into a valuable resource." Research on MDF Recycling
Final thoughts
Medium-Density Fibreboard represents a significant innovation in engineered wood products, offering an effective solution to many of the limitations and inconsistencies of natural timber.
Its exceptional uniformity, smooth surface, and excellent machinability have revolutionised the interior trim and furniture industries, making high-quality painted finishes more accessible and affordable. The variety of specialised grades ensures there's an MDF variant suitable for nearly any interior application.
Yet, MDF is not without limitations. Its performance in wet environments, lower strength-to-weight ratio compared to plywood, and specific health considerations during machining all require acknowledgment. Understanding these characteristics, both strengths and limitations, is key to making informed material choices.
Explore our range of MDF products
From skirting boards and architraves to wall panelling, our premium MDF mouldings combine quality materials with expert manufacturing.
References
- Natural Resources Canada. (2025). Medium-density fibreboard. https://natural-resources.canada.ca/forest-forestry/forest-industry-trade/medium-density-fibreboard
- Wood Panel Industries Federation. (2024). Industry Statistics. https://wpif.org.uk/Industry_Statistics.html
- British Standards Institution. (2009). BS EN 622-5:2009 Fibreboards - Specifications - Part 5: Requirements for dry process boards (MDF).
- Health and Safety Executive. (2024). Woodworking - Hazardous substances. https://www.hse.gov.uk/woodworking/hazard.htm
- Skeg, R., Jones, D., & Hughes, M. (2023). Developments in the Recycling of Wood and Wood Fibre in the UK: A Review. Fibres, 13(2), 23. https://www.mdpi.com/2079-6439/13/2/23






