
HDF vs MDF | High-Density Fibreboard | Everything You Need To Know
Posted by Skirting World on 22nd Feb 2024
HDF and MDF have both dominated the engineered wood board industry and market since the 1980s. Their popularity is a result of their machinability, affordability, weight, density and several other critical factors.
Both HDF and MDF are very similar in structure and formation, yet have drastically different uses, it takes a trained eye and experience to master the use of these fibreboards.
Read on to learn more about HDF, MDF and other engineered wood products such as LDF, OSB, Particle Board. We'll explore the specifications of each board, their practicalities and use cases, strengths and weaknesses in construction and more!
HDF - High Density Fibreboard
HDF Full Form: High-Density Fibreboard
HDF, which stands for High-Density Fibreboard, is a type of engineered wood board, specifically a fibreboard. HDF was originally known as 'Hardboard', by its accidental inventor William Mason in 1925. William later trademarked the name 'Masonite', which is also a generic term for HDF in the US and Canada.
HDF is similar to MDF (Medium-Density Fibreboard) and LDF (Low-Density Fibreboard / also known as Particle Board). And as the names suggest, their primary difference is the density of the wood fibres which compose the fibreboard.
Flat Side Of A HDF Hardboard
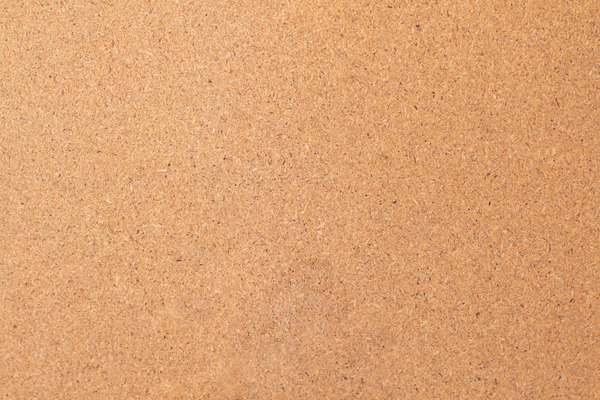

HDF boards have a consistent smooth appearance and texture due to the fineness of the wood fibres used in their construction. This side is ideal for painting due to its uniform surface.
The Textured Side Of A HDF Hardboard
Not all HDF boards have a textured side, of the boards which do, the wood fibres come into contact with a screen or rollers when compressed, which leaves a patterned impression. This texture can help the board grip adhesives or other materials better.
How HDF Is Made
HDF is made from two main components. Wood fibre and resin.
Wood Fibre
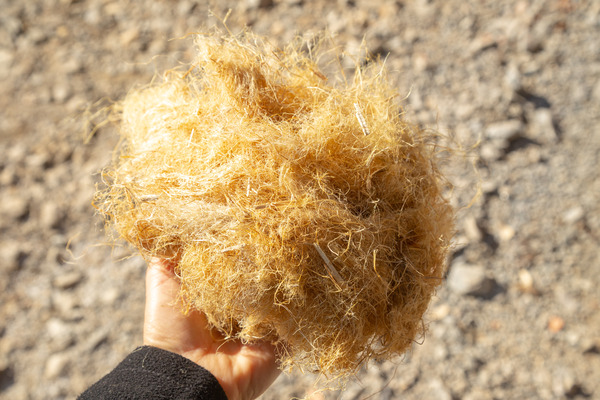

Shredded/pulled wood fibres prior to the chemical pulping stage
Wood fibre is the raw material for HDF, usually obtained from various softwoods such as Pine, Fir or Spruce. Hardwoods like Oak and Birch and recycled wood from sawdust, wood chips and wood waste are sometimes used.
The wood fibre is refined into ultra-fine particles using mechanical or chemical processes such as chipping, grinding or pulping. The mechanical process involves cutting or shredding the wood into small pieces, while the chemical process involves cooking the wood in a solution of water and chemicals to dissolve the lignin and separate the fibres.
The refining process affects the quality and characteristics of the wood fibres, such as the length, width, thickness, surface area and bonding potential. Generally, longer and thinner fibres have higher strength, whilst shorter and thicker fibres have higher density and stability.
Resin

Urea-formaldehyde resin in a beaker
Resin is the adhesive substance that is mixed into the fibres at specific ratios to bind the wood fibres together, forming a dense and uniform panel. The resin can be synthetic or natural.
The most common type of resin used is urea-formaldehyde, a low-cost and durable synthetic adhesive, but also emits formaldehyde which is a harmful substance which can degrade indoor air quality. Other types of resin used for HDF include melamine-formaldehyde, phenol-formaldehyde, lignin, wax and starch.
The ratio of resin to fibres varies on the types of wood and resin used. For every 100 grams of HDF, there are usually 10 - 20 grams of resin and 80 - 90 grams of fibre.
The ratio of resin to fibre by volume can be derived from the ratio of resin to fibres by weight, using the densities of resin and fibre. The ratio of resin to fibres by volume can range from 30% to 50%, depending on the density and type of resin and fibres. This means that for every 100 cubic centimetres of HDF, there are 30 to 50 cubic centimetres of resin and 50 to 70 cubic centimetres of fibre.
Forming The HDF Panels - An 8 Step Process
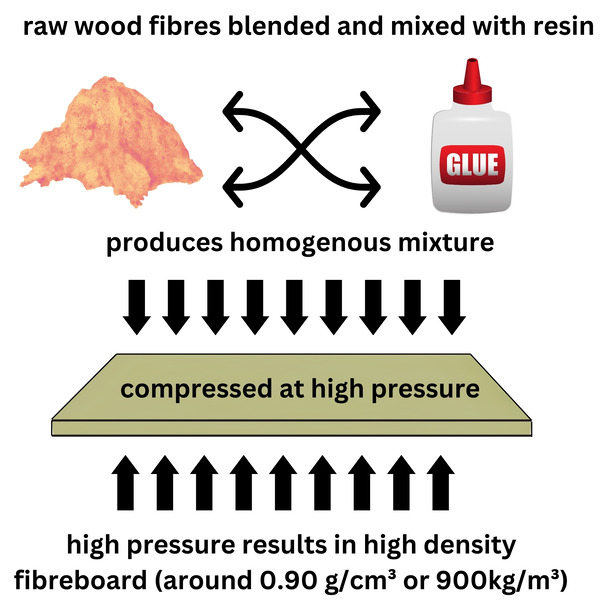
Industrially HDF, MDF and LDF is mass-produced from wood fibres and resin with the following steps.
1. Preparation
The raw material for HDF, wood fibre and resin, are prepared and stored in silos or tanks. As detailed above, the wood fibre is obtained from various sources and the resin is obtained from synthetic or natural sources, then mixed with additives and catalysts to improve the bonding and curing properties.
2. Blending
The wood fibre and resin are blended together in a specific ratio depending on the desired properties or grade of the HDF sheet. The blending can be done using drum blenders, disc blenders or air blenders. The blending process ensures a uniform distribution of resin and fibre, contributing to the creation of a homogenous mixture.
3. Forming
The resulting wood fibre / resin mixture is formed into a continuous mat or sheet using a forming machine. The forming machine can be either a single-opening or multi-opening press, depending on the production capacity and efficiency. The forming machine applies heat and pressure to the mixture. Causing the resin to melt and bond the fibres together.
The forming machine also controls the thickness and density of the HDF panel, by adjusting the speed and pressure of the press.
4. Cooling
The HDF panel is cooled to room temperature using a cooling system. The cooling system prevents the HDF panel from warping or cracking due to thermal stress and stabilises its dimensions and properties.
5. Cutting
After the HDF panel is cooled, it's cut into the required size and shape. The cutting process can also create different types of edges, such as square, bevelled or tongue-and-groove, depending on the intended use of the HDF panel.
6. Sanding
After the HDF panel is cut, it is sanded to achieve a smooth surface, using abrasive belts, discs or rollers. The sanding process removes any defects such as roughness, unevenness or scratches and improves the appearance of the panel.
7. Treating
After sanding, the panel can be further treated with various coatings, laminates, veneers or paints to enhance its appearance, durability and functionality. The treating process can provide different types of finishes such as glossy, matte, textured or patterned. It can also protect the HDF panel from moisture, stains, scratches or UV rays and increase resistance to wear and tear.
8. Testing
The physical and mechanical properties can be determined and verified through testing. Characteristics and qualities such as density, moisture content, bending strength, modulus of elasticity, internal bond strength, surface soundness, formaldehyde emission and more can be determined to establish a grade. Testing is vital to ensure the panels meet required standards, regulations and their suitability for the intended application.
The processes for making HDF, MDF and LDF are virtually identical, the primary difference is the pressing of the panels and the quantity of mixture used per panel to form either a high, medium or low density panel.
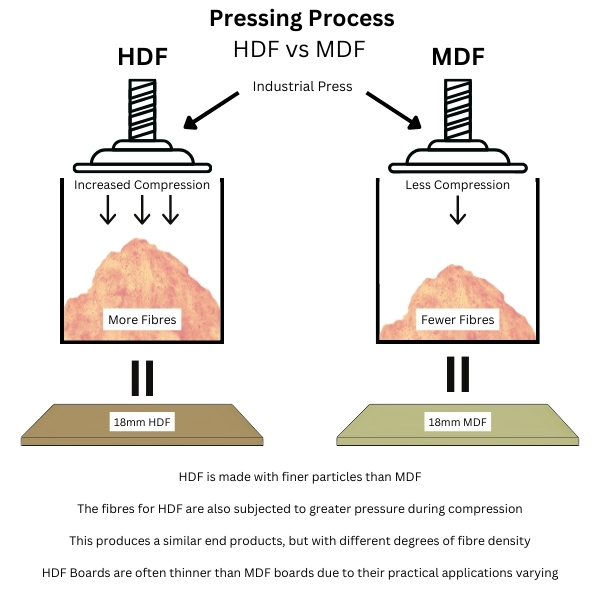
HDF vs MDF - The Difference
MDF Full Form: Medium-Density Fibreboard
HDF (High-Density Fibreboard) and MDF (Medium-Density Fibreboard) are both types of engineered wood fibreboards. Both are widely used in construction and design, whilst they share similarities in composition, their primary difference is density, which leads to distinct properties and applications.
| HDF | MDF | |
|---|---|---|
| Density & Strength | Higher density and strength, resistant to warping | Less dense and strong, prone to chipping |
| Moisture Resistance | More resistant to moisture and humidity | Less resistant to moisture and prone to warping |
| Applications | High-traffic areas, durable applications, laminated flooring | Furniture, cabinetry, decorative applications |
| Machinability & Finishing | More difficult to machine and finish | Easy to machine and finish, smooth surface |
| Cost | More expensive | More affordable |
| Sustainability | Sustainable and eco-friendly | Sustainable and eco-friendly |
Density: The Defining Difference Between HDF & MDF
The primary differentiator between HDF and MDF is their density. As its name suggests, HDF exhibits a higher density than MDF due to the tighter compaction of its wood fibres. This density difference translates to the following qualities:
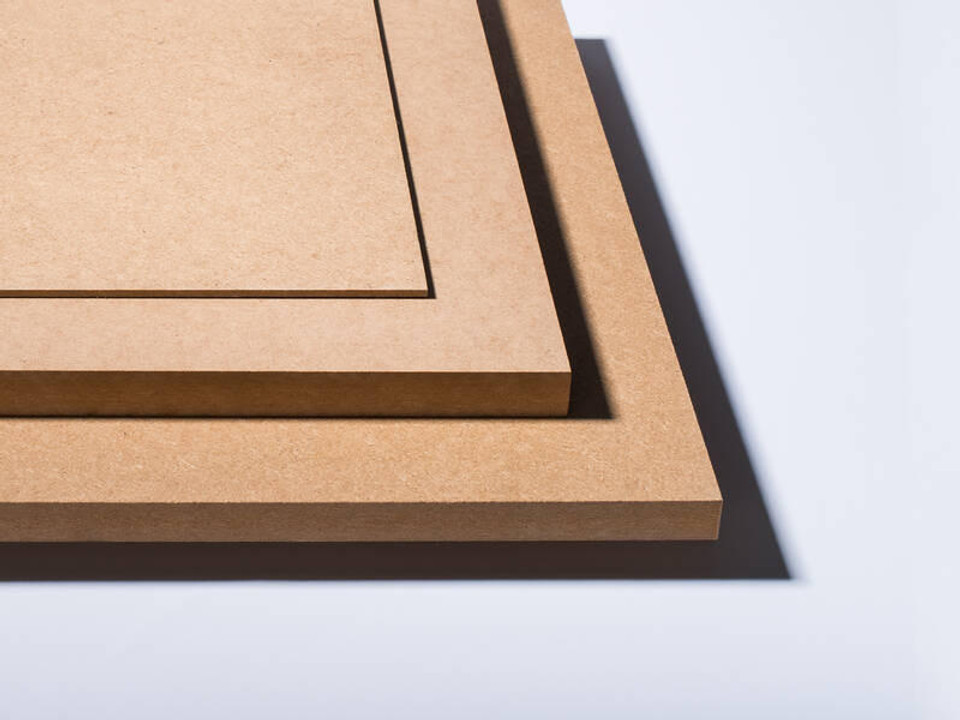

HDF's Unique Qualities
HDF has a higher density than MDF, which gives it unique advantages.
Density Of HDF: Standard HDF (High-Density Fibreboard) has a density of 880 - 1040 kg/m³ (55-65 lbs/ft³)
- Strength & Durability: HDF is stronger and more durable than MDF due to its higher density and smaller wood fibres. HDF is less prone to chipping, cracking, and warping than MDF, and is better suited for applications where strength and durability are essential.
- Hardness: HDF's tight fibre structure yields a harder surface, allowing for precise machining and sharp edges. This characteristic lends itself well to applications requiring intricate details, such as millwork and mouldings.
- Density & Weight: HDF is denser and heavier than MDF due to its smaller and more tightly packed wood fibres. HDF typically has a density of around 50-65 pounds per cubic foot, while MDF has a density of around 30-50 pounds per cubic foot.
- Edge Holding: HDF excels in holding sharp, crisp edges due to its dense composition, crucial for intricate detailing
- Stability: The tighter fibre structure of HDF minimises movement and warping, making it suitable for dimensional stability requirements
- Moisture Resistance: Neither material excels in moisture resistance, but HDF exhibits slightly better performance due to its denser structure.
MDF's Unique Qualities
MDF has a lower density compared to HDF, offering distinct advantages:
Density Of MDF: Standard MDF (Medium-Density Fibreboard) has a density of 800-880 kg/m³ (50-55 lbs/ft³)
- Workability: MDF's looser fibre structure makes it easier to cut, mitre, shape, and machine than HDF. This characteristic favours its use in furniture construction, cabinetry, and decorative applications.
- Smoothness: MDF's inherent smoothness creates an ideal surface for painting, veneering, and applying laminates. This versatility allows for diverse aesthetic finishes.
- Weight: The lighter weight of MDF compared to HDF simplifies handling and installation, making it a practical choice for various applications.
- Machinability: MDF's looser fibre structure allows for easier cutting, shaping and drilling, making it ideal for intricate designs and woodworking projects.
Neither HDF or MDF are water-resistant, both boards suffer from swelling and water damage when soaked in water or with prolonged exposure. However, higher grade MDF can be treated to be moisture-resistant, which allows for installation in environments such as kitchens and bathrooms, outside of direct contact with water.
HDF Grades vs MDF Grades
HDF Grades
HDF generally has fewer grades on the market, although you can find a variety of HDF products, the main grades are Standard HDF and Ultra-High Density HDF.| Grade | Density (kg/m³) | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard HDF | 800-900 | Good strength, rigidity, stability, machinability, screw holding, edge definition, moderate moisture resistance, smooth, paintable | Furniture, cabinets, doors, trim, interior uses |
| Ultra-High Density HDF (UHDF) | Over 1100 | Excellent strength, rigidity, stability, machinability, screw holding, edge definition, high moisture resistance, very smooth, paintable | High-end furniture, cabinets, musical instruments, speaker boxes, demanding applications |
MDF Grades
MDF, being the more popular variant of fibreboard, is available in a wide variety of grades.
| Grade | Density (kg/m³) | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard MDF | 600-800 | Good strength, stiffness, machinable, paintable, can be veneered | Furniture, cabinets, doors, trim, general-purpose |
| High-density MDF (HD MDF) | 800-1100 | Denser, stronger, improved screw holding, edge definition, more moisture resistant | Furniture, cabinets, doors, trim, high-end joinery, demanding applications |
|
|
|||
| Flame-retardant MDF (FR MDF) | Varies | Fire-retardant additives, meets building codes | Wall panels, ceilings, doors (fire safety concern) |
| Moisture-resistant MDF (MR MDF) | Varies | Treated resins, waxes for improved moisture resistance | Kitchens, bathrooms, humid environments |
| Veneered MDF | Varies | Thin layer of real wood veneer on surface | Furniture, cabinets, doors, trim (desired real wood look) |
| Melamine MDF | Varies | Melamine laminate applied to surface (durable, scratch-resistant, moisture-resistant) | Furniture, cabinets, countertops (durable, easy-to-clean) |
A popular grade of MDF on the market is High Density MDF, the terms can become a little confusing, however HD-MDF is simply MDF pressed to a higher density than standard, often to the same density as HDF, without possessing the same fibre qualities and unique characteristics of HDF Hardboard. Consider HD-MDF as a superior quality MDF which has increased strength, durability and a more consistent, smooth finish.
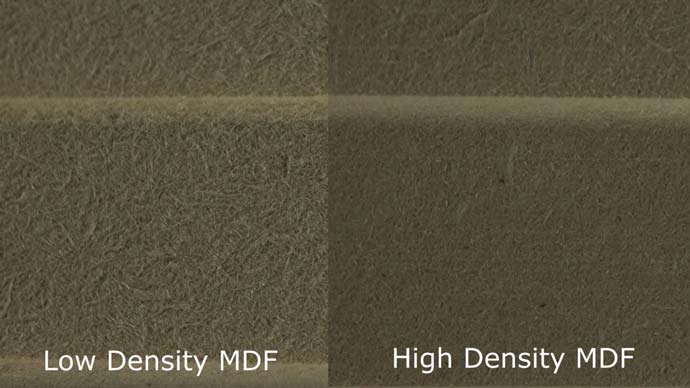
LDF - Low Density Fibreboard
LDF stands for Low-Density Fibreboard, also known as Particle Board. As the name suggests, the fibres are more loosely pressed, LDF has a lower density and is less rigid than medium or high-density fibreboard. LDF is lightweight and easier to cut, shape, and nail compared to higher density boards. It also has enhanced acoustic properties. Common uses for LDF include furniture, shelving, partition walls, sound deadening boards, and underlay materials due to its lower cost and workability.
The looser bonding however means LDF lacks the strength and hardness required for structural builds or high wear applications. Proper sealing and moisture protection should be applied, as LDF is prone to expansion and deterioration when exposed directly to water over time.
Fibreboard Specification Sheets
Below are three specification sheets for HDF, MDF and LDF (Low-Density Fibreboard) from Roseburgs line of engineered wood boards.
| HDF Specification Sheet | Physical Properties (Metric) |
| Density | 892 Kg/m³ |
| Moisture Content | 5% |
| Thickness Tolerance | ± 0.125 mm |
| Modulus Of Rupture | 35.8 N/mm² |
| Internal Bond | 1.06 N/mm² |
|
Linear Expansion Limit |
≤ 0.3% |
| Length / Width Tolerance | ± 1.8mm |
| Thickness Swell | ≤ 0.087" ppm |
| MDF Specification Sheet | Physical Properties (Metric) |
| Density | 788 Kg/m³ |
| Moisture Content | 5.5% |
| Thickness Tolerance | ± 0.125 mm |
| Modulus Of Rupture | 33.1 N/mm² |
| Internal Bond | 0.9 N/mm² |
|
Linear Expansion Limit |
≤ 0.3% |
| Length / Width Tolerance | ± 1.8mm |
| Thickness Swell | ≤ 1.3mm" |
| LDF Specification Sheet | Physical Properties (Metric) |
| Density | 724 Kg/m³ |
| Moisture Content | 5.5% |
| Thickness Tolerance | ± 0.125 mm |
| Modulus Of Rupture | 24.1 N/mm² |
| Internal Bond | 0.76 N/mm² |
|
Linear Expansion Limit |
≤ 0.3% |
| Length / Width Tolerance | ± 1.8mm |
| Thickness Swell | ≤ 1.3mm" |
Specification Breakdown
- Density: Reflects the board's mass per unit volume. HDF has the highest density at 892 kg/m³, making it heavier and typically more durable than MDF (788 kg/m³) and LDF (724 kg/m³).
- Moisture Content: Indicates the percentage of water in the board, affecting its stability and resistance to warping. All three types have similar moisture content, with HDF at 5% and both MDF and LDF at 5.5%, suggesting comparable stability.
- Thickness Tolerance: The acceptable variation in the board's thickness. All types have a tolerance of ±0.125 mm, showing they are manufactured to precise standards.
- Modulus Of Rupture: Measures the board's strength before breaking when bent. HDF is the strongest (35.8 N/mm²), followed by MDF (33.1 N/mm²) and then LDF (24.1 N/mm²), indicating HDF is better for high-stress applications.
- Internal Bond: The strength of the bond between the board's fibers. HDF again leads with 1.06 N/mm², MDF is next at 0.9 N/mm², and LDF is at 0.76 N/mm², suggesting HDF has the highest internal cohesion.
- Linear Expansion Limit: The rate at which the board expands due to changes in humidity or temperature. All boards have a similar expansion limit of ≤0.3%.
- Length/Width Tolerance: The allowable variance in the board's dimensions. All types have a tolerance of ±1.8mm, indicating uniformity in size.
- Thickness Swell: Indicates how much the board's thickness increases after exposure to moisture. HDF has the least swell (≤0.087" ppm), followed by MDF and LDF (both ≤1.3mm), showing HDF is more resistant to moisture-induced swelling.
Conclusion
In conclusion, HDF and MDF are both popular choices for interior design and furniture projects, but there are important differences between the two materials. HDF is denser and stronger than MDF, making it well-suited for high-traffic areas and applications where durability is essential.
MDF, on the other hand, is a more versatile and affordable option that is ideal for applications where a smooth and uniform surface is required.
When choosing between HDF vs MDF, it is important to consider the specific needs of your project, such as the desired finish, the level of durability required, and your overall budget. While HDF may be more expensive than MDF, it is a better choice for applications where strength and durability are essential.
MDF is a more affordable option that is well-suited for a wide range of interior design and furniture projects.








